What Does Source water assessment and protection (SWAP) Mean?


PLATFORM: Visible But Unseen: The Material Cultures of Los Angeles's Indoor Swap Meets
swap meaning and definition
Excitement About Swap - Raydium
4 112. 1 13. 0 18. 9 23. 7 33. 4 44. 8 74. 4 97. 6 11. 1 10. 1 12. 8 17. 4 21. 5 25. 6 38. 0 4. 0 5. 0 6. 2 7. 9 11. 6 15. 1 22. 3 1. 1 1. 2 1.

What is a swap? – US.CAPITAL BANK N A
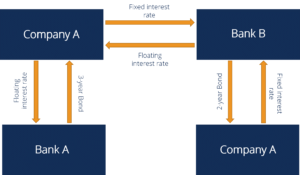
0 2. 7 3. 3 3. 5 Source: "The Global OTC Derivatives Market at end-December 2004", BIS, , "OTC Derivatives Market Activity in the 2nd Half of 2006", BIS, Major Swap Individual [modify] A Major Swap Individual (MSP, or sometimes Swap Bank) is a generic term to explain a banks that facilitates swaps in between counterparties.
A swap bank can be a worldwide commercial bank, a financial investment bank, a merchant bank, or an independent operator. A swap bank works as either a swap broker or swap dealership. As a broker, the swap bank matches counterparties however does not assume any danger of the swap. The swap broker gets a commission for this service.
5 Simple Techniques For Swap Your Phone - Mobile Trade-in Deals - Visible
As a market maker, a swap bank wants to accept either side of a currency swap, and then later on on-sell it, or match it with a counterparty. In this capability, the swap bank presumes a position in the swap and for that reason assumes some risks. The dealer capacity is undoubtedly more risky, and the swap bank would get a portion of the cash flows passed through it to compensate it for bearing this risk.
These reasons seem straightforward and hard to argue with, particularly to the degree that name acknowledgment is really essential in raising funds in the international bond market. Companies using currency swaps have statistically higher levels of long-term foreign-denominated debt than firms that use no currency derivatives. On the other hand, the primary users of currency swaps are non-financial, worldwide companies with long-lasting foreign-currency funding needs.
Financing foreign-currency debt using domestic currency and a currency swap is for that reason superior to financing directly with foreign-currency debt. The 2 primary factors for switching rates of interest are to much better match maturities of assets and liabilities and/or to acquire an expense savings through the quality spread differential (QSD). This Is Noteworthy recommends that the spread between AAA-rated industrial paper (floating) and A-rated commercial is somewhat less than the spread between AAA-rated five-year commitment (repaired) and an A-rated responsibility of the very same tenor.

